The base rate reduced to 15.75 %
The Monetary Policy Committee of the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan has made a decision to reduce the base rate to the level of 15.75% per annum with the interest rate corridor of +/– 1 percentage point. The decision was made based on updated forecasts of the National Bank, data analysis and assessment of the balance of inflation risks.
The annual inflation continues to dynamically decelerate. The indicator is expected to move into the single-digit zone in the coming months. Monthly inflation in October slowed down to historically average levels. External inflationary pressures continue to ease amid the restraining policies of central banks and a decline in global food prices. However, there are specific factors and risks that require attention. In the domestic economy, pro-inflationary pressure persists due to fiscal stimulus, sustained internal demand, and high and unstable inflation expectations.
Further decisions on the base rate will depend on the alignment of the actual inflation dynamics with its forecasted trajectory. The necessity to achieve the inflation target of 5% requires the maintenance of moderately tight monetary conditions in the medium term.
In October 2023, the annual inflation continued its deceleration, reaching 10.8%, which is closer to the lower bound of the previous forecasted range. The monthly inflation for October 2023 was 0.7%, declining to levels of its average historical values. The slowdown in price growth is attributed to the implemented monetary policy, the reduction of global inflationary pressures and production costs, the gradual restoration of logistical chains, government measures, as well as the influence of the high base effect from the previous year. Both core and seasonally-adjusted inflation indicators have stabilized but persistently remain above the target, reflecting sustained price increases across a broad range of goods and services.
Despite the consistent deceleration of inflation, public inflation expectations remain elevated and sensitive to changes in individual commodity markets. In October 2023, the year-ahead expected inflation accelerated. The main factors for increased expectations remain the rise in prices for gasoline and the dynamics of food prices.
Global inflation has continued to decelerate. Many countries, including a significant portion of trading partners, are experiencing a trend of slowing inflation. However, there are persistent risks of increased external inflationary pressure due to the higher inflation in Russia compared to the previous forecast. In the medium term, pro-inflationary pressure is expected to weaken as inflation in trading partner countries approaches the target. The FAO Food Price Index is decreasing, driven by declines in sugar, grains, vegetable oils, and meat prices. It is anticipated that grain prices will decrease due to seasonal increases in supply, but by the end of 2023 and the beginning of 2024, prices are expected to rise due to lower grain supplies from Ukraine. From mid-2024 onward, a gradual decline in grain prices is expected due to increased supply and improved logistical chains.
External monetary conditions remain tight. Uncertainty regarding the future dynamics of inflation is once again delaying the onset of the interest rate cut cycle by the U.S. Federal Reserve to a later date. The European Central Bank (ECB) intends to maintain a policy of high rates for a longer period. In some trading partner countries, monetary policy continues to tighten amid inflation exceeding target values.
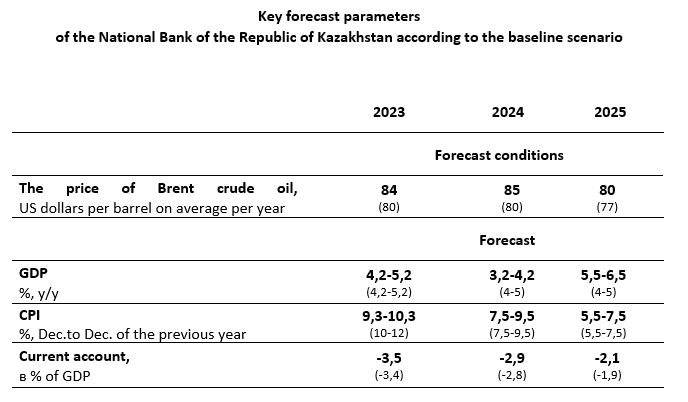
The baseline scenario envisions the stabilization of Brent crude oil prices by the end of the current year within the range of $85-90 per barrel against the backdrop of the extension of OPEC+ production cuts and ongoing military actions in the Middle East. Under the baseline scenario, in 2024 and 2025, due to moderate energy demand in the context of weaker global economic growth, it is assumed that the price of Brent crude oil will gradually decrease to $85 and $80 on average per year, respectively.
The inflation forecast for 2023 has been improved to a range of 9.3-10.3%. The adjustment in the 2023 forecast is attributed to a more moderate than expected increase in utilities tariffs and a more restrained rise in prices for non-food goods. The forecast for 2024 remains at a level of 7.5-9.5%, and for 2025, it is maintained at 5.5-7.5%. Key risks to the inflation forecast for 2024-2025 include the increased fiscal stimulus, unanchored inflation expectations, potential food price increases due to the effect of low harvest in 2023, as well as direct effect of rising utilities tariffs. The inflation forecast also does not take into account the increase in VAT in 2025, discussed by the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
The economic growth forecast for Kazakhstan in 2024 and 2025 has been revised. This year, GDP growth, as before, is expected at the level of 4.2-5.2%. The forecast for 2024 has been reduced to 3.2-4.2% due to the possible postponement to the end of 2024 or 2025 of the start of an increase in production at TCO. Against this background, taking into account the effect of a lower base, the forecast for 2025 has been raised to 5.5-6.5%. The main and significant factor that increases the risks of the forecast is the uncertainty regarding the parameters of oil production in 2024-2025.
The dynamic decrease in annual inflation and its lower forecasts until the end of 2023 have created room for the base rate cut. Future decisions regarding the base rate will depend on the alignment of the actual inflation dynamics with its forecasted trajectory. In the event of inflation deceleration in 2024, the National Bank will consider the feasibility of a gradual base rate cut, taking into account the need to maintain moderately tight monetary conditions in the medium term to bring inflation back to the 5% target and anchor inflation expectations. However, for the accumulation of data and monitoring risk balance, pauses in adjusting the base rate are not ruled out.
The key parameters of the forecast are provided in the appendix to the press release. More comprehensive information about the factors influencing the decision and the forecast will be presented in the Monetary Policy Report on the official website of the National Bank[1] on December 4, 2023.
The next scheduled decision of the Monetary Policy Committee of the National Bank of Kazakhstan on the base rate will be announced on January 19, 2024, at 12:00 Astana time.
[1] https://www.nationalbank.kz/en/page/obzor-inflyacii-dkp
More detailed information for the mass media representatives is available upon request:
+7 (7172) 775 210
e-mail: press@nationalbank.kz
www.nationalbank.kz
Appendix